Download
As solar technology advances, PV systems are becoming a cornerstone of residential and commercial projects. However, the quality of a PV system's construction is crucial to ensuring its safety, efficiency, and long-term performance. Drawing on years of on-site maintenance experience, Solis has identified recurring issues in photovoltaic system construction. Here, we explore these common challenges and provide actionable solutions to help ensure your PV project's success.
Electrical Construction Challenges
Electrical faults are one of the leading causes of inefficiency in PV systems. These faults, often found on the DC and AC sides, can significantly impact a system's performance. Let's break them down:
DC Side Challenges
-Connector Mismatches
Using connectors from different manufacturers can result in size and specification mismatches. These mismatches increase contact resistance, leading to overheating and reduced power generation efficiency.
-Improper MC4 Plug Installation
Secure connections require DC plugs to be crimped with specialized tools. Non-standard tools, such as pliers, result in unreliable connections and higher failure rates.
-Cable Management
It's essential to use correctly rated cables with clearly marked polarity (+/-) to prevent wiring errors. Hanging or unsecured cables are prone to physical damage, posing safety risks and reducing reliability.
AC Side Issues
AC-side problems are often linked to improper cable selection, loose connections, or poor installation practices. Recommendations include:
-Use cables with sufficient capacity, following the torque specifications outlined in product manuals (e.g., for Solis S6-GR1P inverters).
-Avoid excessive stress on cables during installation, which can loosen connections over time.
Electrical Construction Pitfalls
Electrical faults are a leading cause of PV system inefficiencies, with most issues stemming from the DC side. Key problems include:
DC Side
Terminal interlocking issues: Using connectors from different manufacturers can lead to size mismatches, increased contact resistance, and overheating, all of which diminish power generation efficiency.
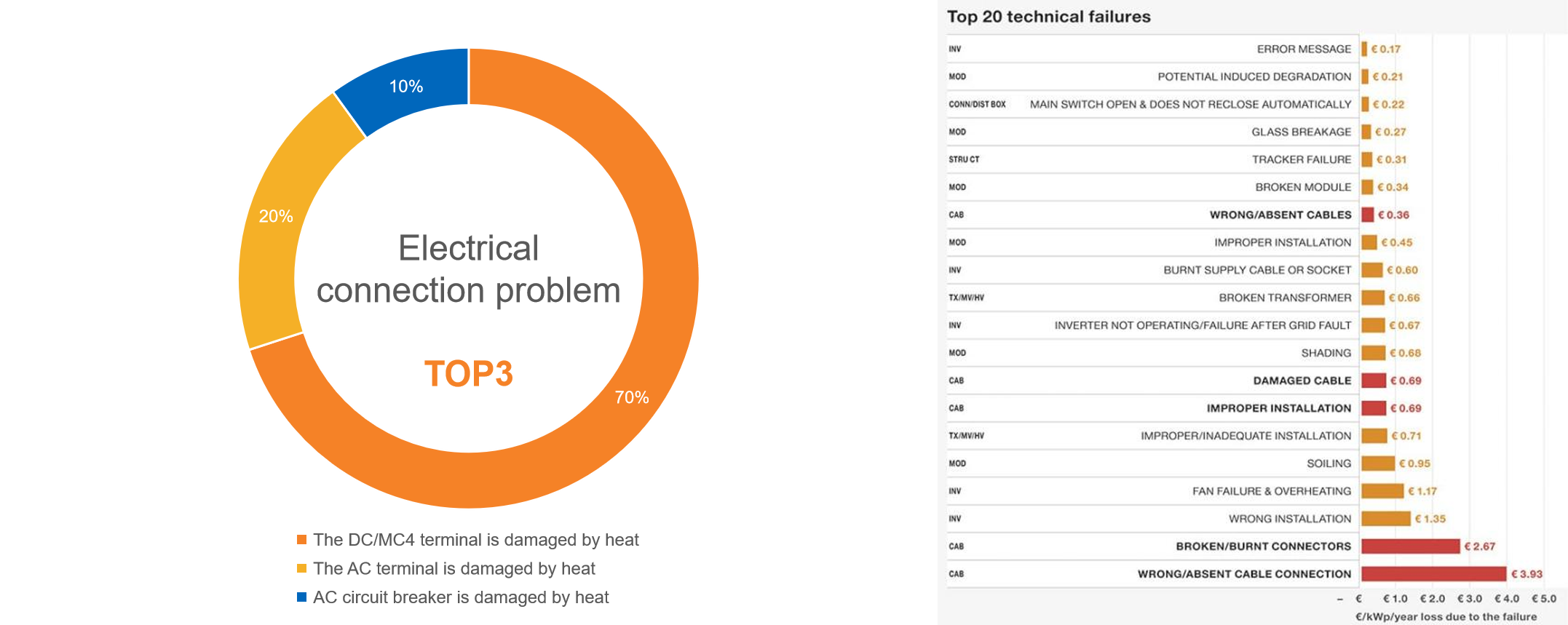
Among them, the DC side, terminal overheating damage mainly has the following aspects:
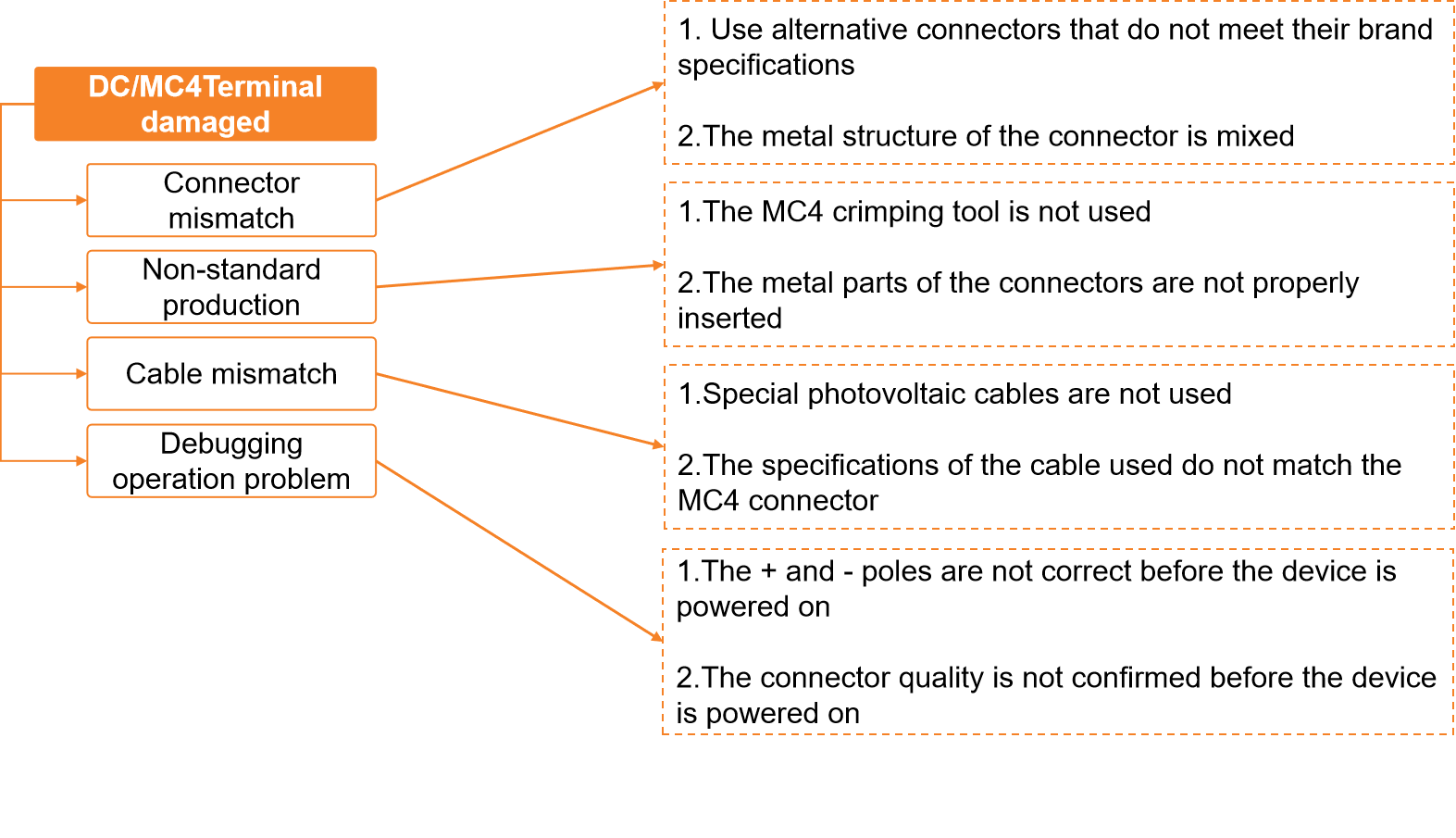
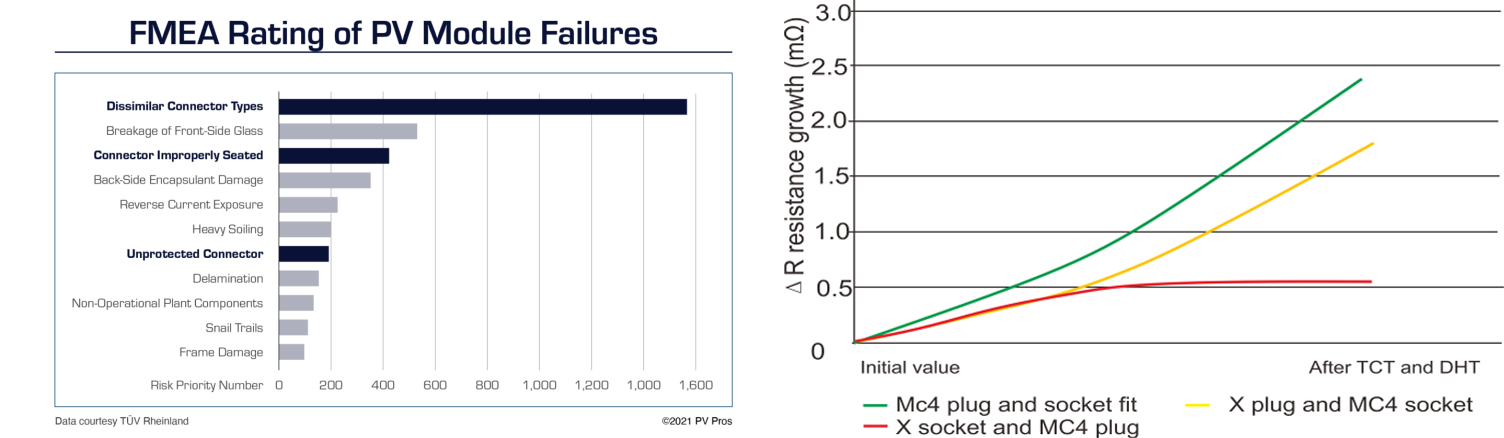
Improper MC4 plug installation: DC plugs should be crimped using specialized tools for secure connections. Using pliers or non-standard tools results in unreliable connections.
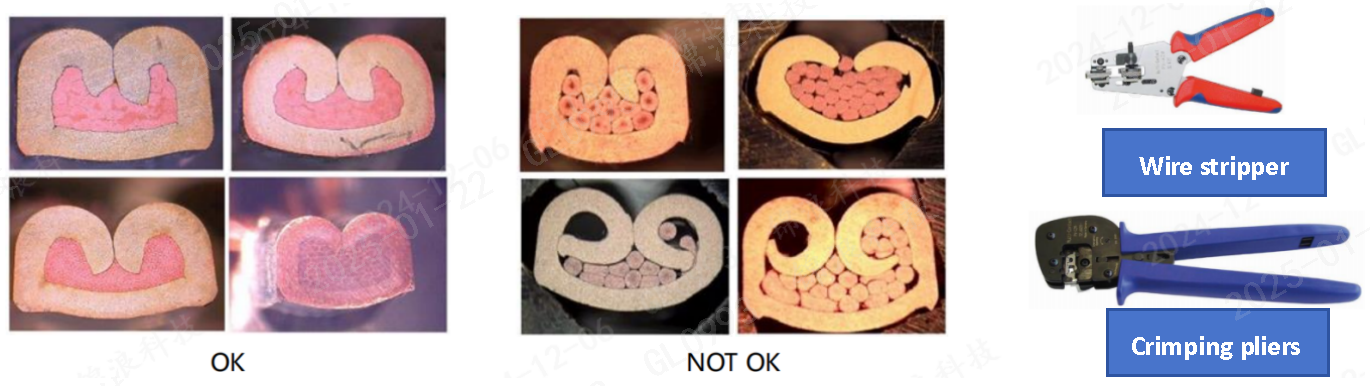
Cable mismatches: Correctly rated cables should be clearly marked with polarity (+/-) to avoid wiring errors. Hanging or unsecured cables are prone to damage, creating reliability concerns.

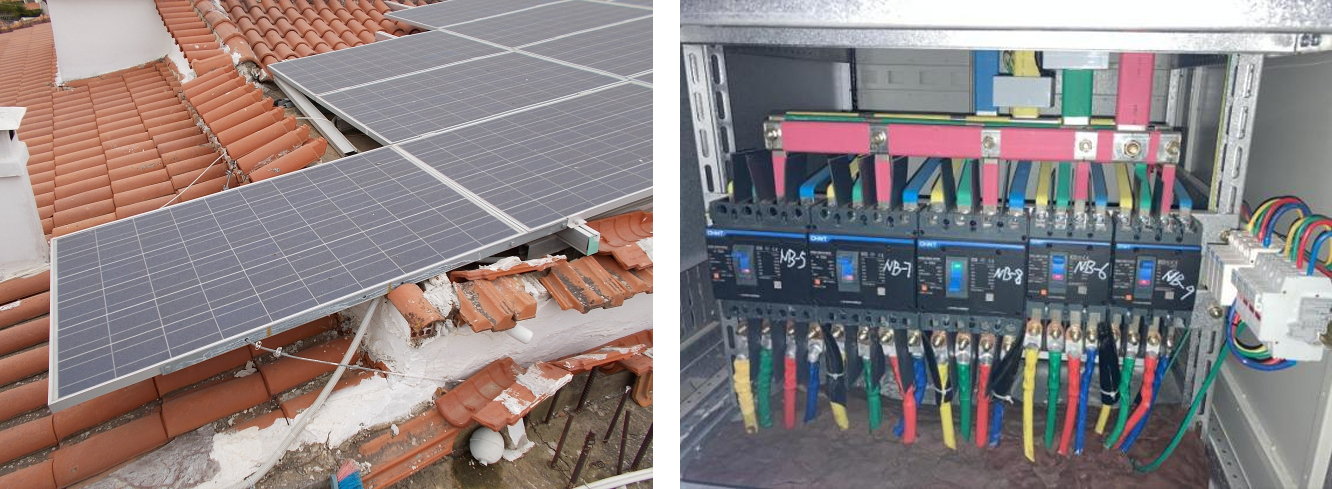
AC side: similar to the DC side, the main problems of AC test are also concentrated in cable selection, wiring operation, laying, etc., in the after-sales field electrical fault statistics, 20% of the electrical problems are concentrated in AC test. Among them, the AC side, terminal overheating damage mainly has the following aspects:
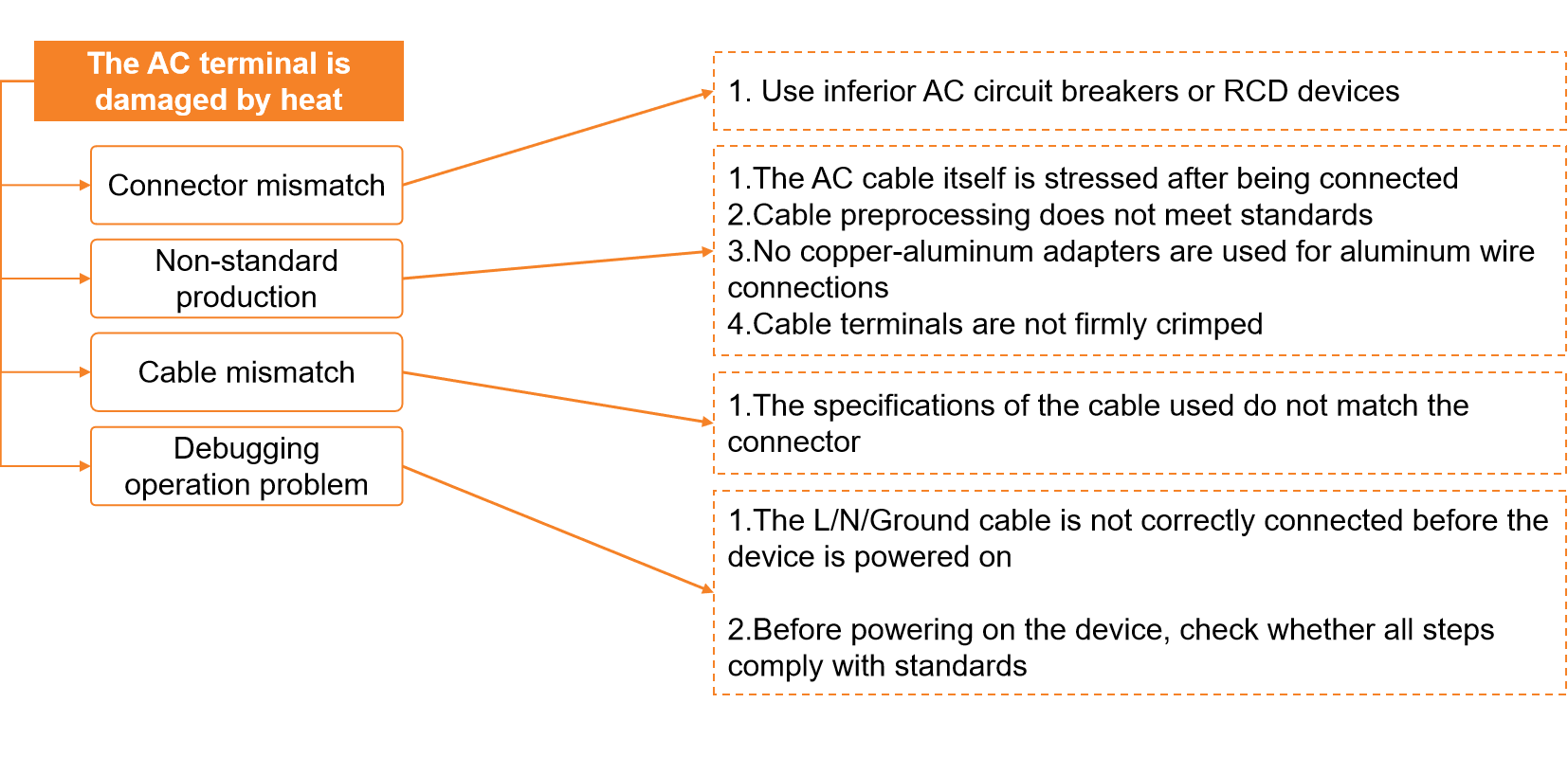
When selecting a cable, ensure that there is sufficient area between the terminal and the cable. For example, S6-GR1P(7-8)K2 is used as an example. The cable model, strip length, and torque are listed in the product manual.

During the installation of the inverter AC cable, avoid excessive stress on cables during installation, which can loosen connections over time.
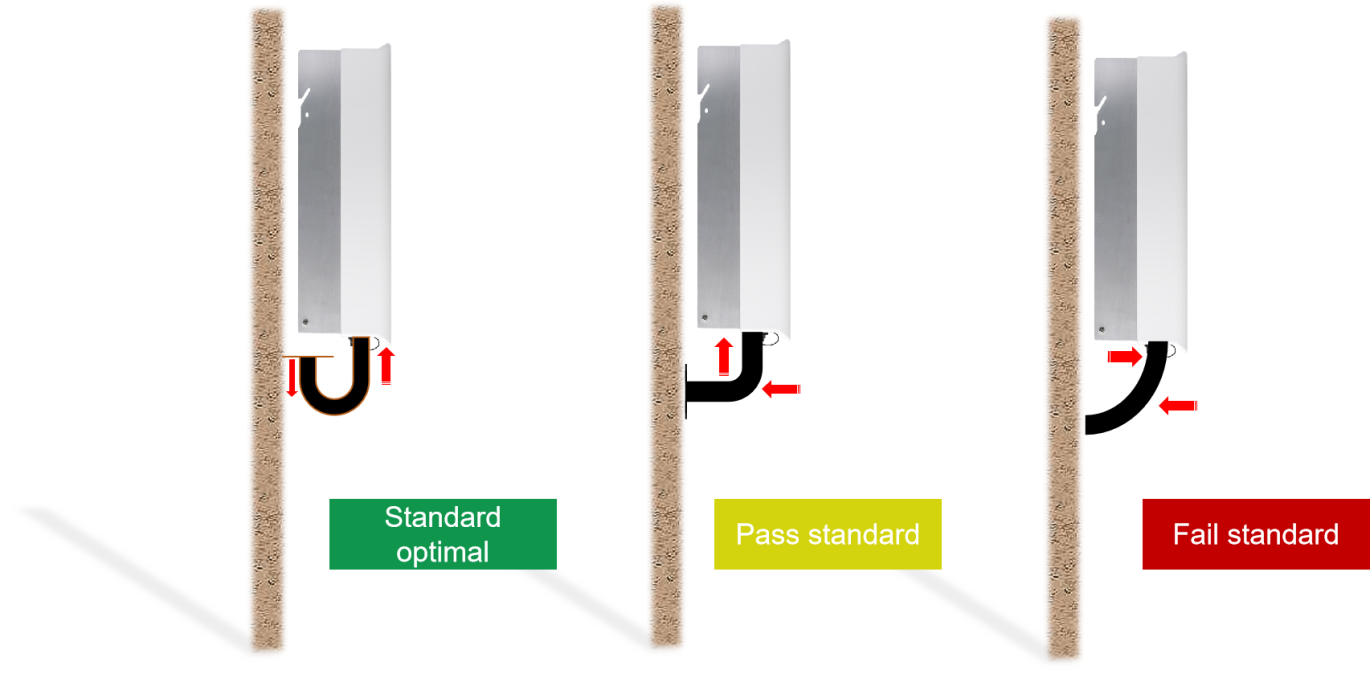
Inverter Installation Best Practices
Proper inverter installation is essential for optimal system performance. Consider the following guidelines:
Placement: Install inverters in dry, well-ventilated locations, such as outdoor walls, rooftops, or equipment rooms. Avoid environments with high humidity, excessive heat, or vibration.
Support: Ensure wall mounts or brackets are secure to prevent movement due to external factors like wind.
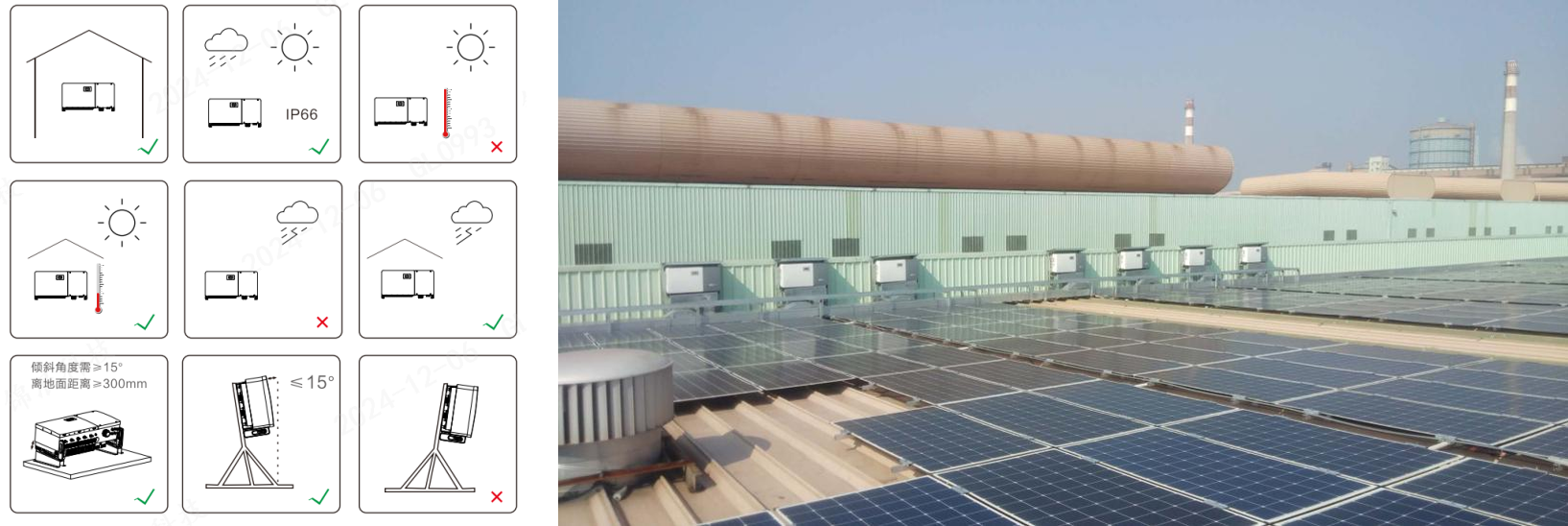

Safety clearances: Maintain adequate space between the inverter and nearby equipment. Protective barriers can prevent unauthorized access or accidental damage.
Weather protection: Use shielding structures to protect inverters from direct sunlight or adverse weather.
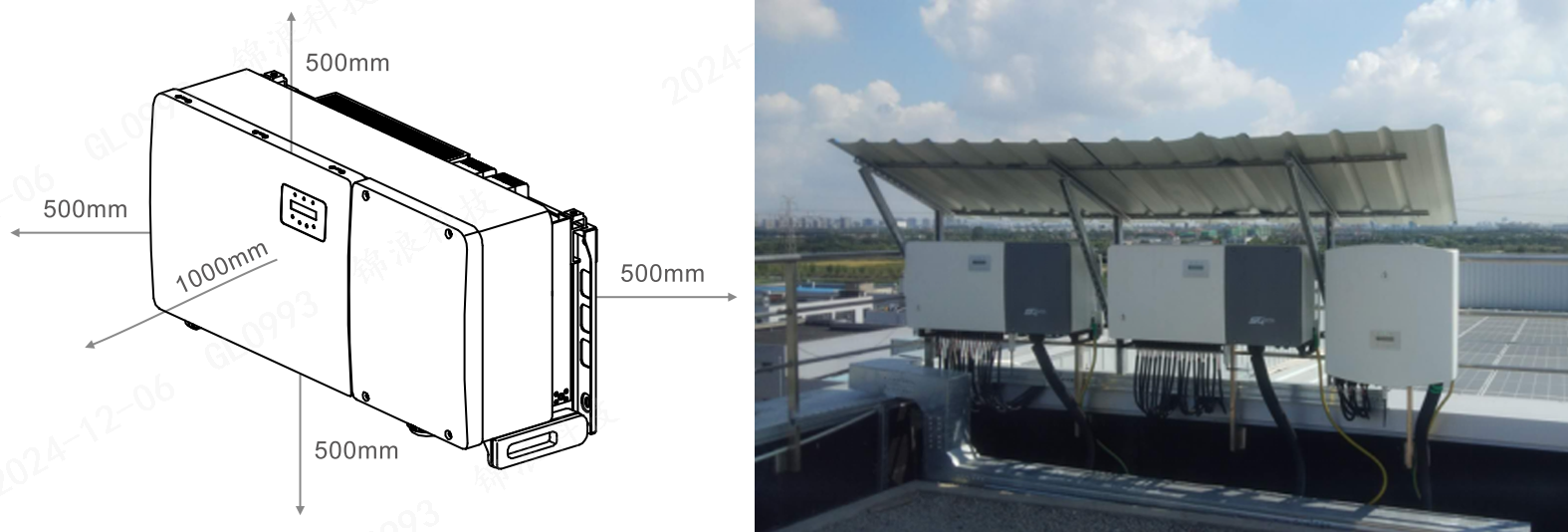
Grounding and surge protection: Proper grounding is essential for electrical safety. Ensure that PV panels, bridge connections, and inverter casings are equipped with grounding jumpers, particularly in industrial and commercial installations. Please refer to previous solis seminars on grounding and lightning protection measures.
Site cleanup: Remove any debris left on or under the PV panels, as this can block components and reduce efficiency.
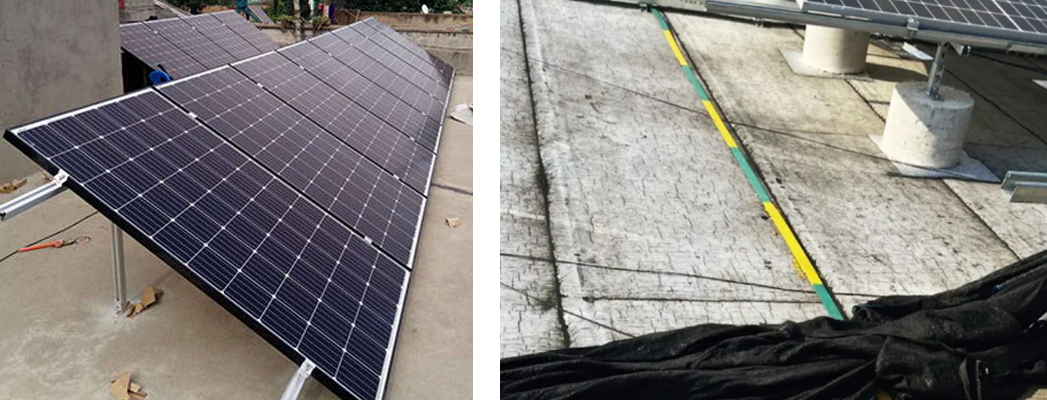

Waterproofing and drainage: Inspect for blocked drainage holes or roof damage. Properly seal cable entry and exit points using approved materials to maintain system integrity.

Conclusion
A high-quality PV system begins with a meticulous construction process. By addressing these common challenges, installers can enhance efficiency, reduce maintenance issues, and ensure the long-term reliability of the system.

 中国
中国
 India
India
 Việt nam
Việt nam
 Australia
Australia
 대한민국
대한민국
 پاکستان
پاکستان
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
Filipino
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Узбекистан
Узбекистан
 Ireland
Ireland
 Türkiye
Türkiye
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 France
France
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Nederland
Nederland
 España
España
 Česká republika
Česká republika
 Sverige
Sverige
 Polska
Polska
 Україна
Україна
 Italia
Italia
 Português
Português
 България
България
 Magyarország
Magyarország
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 United States
United States
 Canada
Canada
 México
México
 Brasil
Brasil
 República de Chile
República de Chile
 South Africa
South Africa
 المملكة العربية السعودية
المملكة العربية السعودية
 الجمهورية اللبنانية
الجمهورية اللبنانية
 امارات عربية متحدة
امارات عربية متحدة
 اليمن
اليمن
 المملكة الأردنّيّة الهاشميّة
المملكة الأردنّيّة الهاشميّة
 جمهورية مصر العربية
جمهورية مصر العربية
 la République Tunisienne
la République Tunisienne
 Kenya
Kenya
 Tanzania
Tanzania
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Other Countries and Regions
Other Countries and Regions