-
Inverter
-
 S6-EH1P(3-6)K-L-EU
S6-EH1P(3-6)K-L-EU
-
 S5-EH1P(3-6)K-L
S5-EH1P(3-6)K-L
-
 RHI-(3-6)K-48ES-5G
RHI-(3-6)K-48ES-5G
-
 S6-EO1P(4-5)K-48
S6-EO1P(4-5)K-48
-
 S6-EO1P(4-5)K-48-EU
S6-EO1P(4-5)K-48-EU
-
 S5-EO1P(4-5)K-48
S5-EO1P(4-5)K-48
-
 S6-EA1P(3.6-6)K-L
S6-EA1P(3.6-6)K-L
-
 S5-EA1P3K-L
S5-EA1P3K-L
-
 S6-EA3P(5-10)KAA-NV-ND-H
S6-EA3P(5-10)KAA-NV-ND-H
-
 S6-EH1P(3-6)K-L-PRO
S6-EH1P(3-6)K-L-PRO
-
 S6-EH1P8K-L-PRO
S6-EH1P8K-L-PRO
-
 S6-EH1P(3-8)K-L-PLUS
S6-EH1P(3-8)K-L-PLUS
-
 S6-EH3P(3-10)K-H-EU
S6-EH3P(3-10)K-H-EU
-
 S6-EH3P(5-10)K2-H
S6-EH3P(5-10)K2-H
-
 RHI-3P(3-10)K-HVES-5G
RHI-3P(3-10)K-HVES-5G
-
 S6-EH1P(12-16)K03-NV-YD-L
S6-EH1P(12-16)K03-NV-YD-L
-
 S6-EH3P(8-15)K02-NV-YD-L
S6-EH3P(8-15)K02-NV-YD-L
-
 S6-EH3P(12-20)K-H
S6-EH3P(12-20)K-H
-
 S6-EH3P(12-20)K-ND-H
S6-EH3P(12-20)K-ND-H
-
 S6-EH3P(8-12)K-LV-ND-H
S6-EH3P(8-12)K-LV-ND-H
-
 S6-EH3P(29.9-50)K-H
S6-EH3P(29.9-50)K-H
-
 S6-EH3P30K-H-LV
S6-EH3P30K-H-LV
-
 S6-EH3P(30-50)K-H-ND
S6-EH3P(30-50)K-H-ND
-
 S6-EH3P(15-30)K-H-LV-ND
S6-EH3P(15-30)K-H-LV-ND
-
 S6-EH3P(80-100)K10-NV-YD-H
S6-EH3P(80-100)K10-NV-YD-H
-
 S6-GR1P0.8K-UM
S6-GR1P0.8K-UM
-
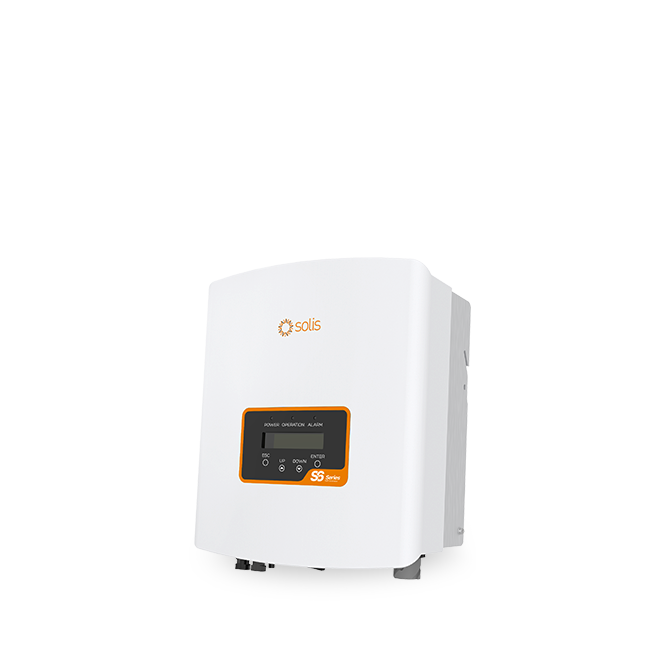 S6-GR1P(0.7-3.6)K-M
S6-GR1P(0.7-3.6)K-M
-
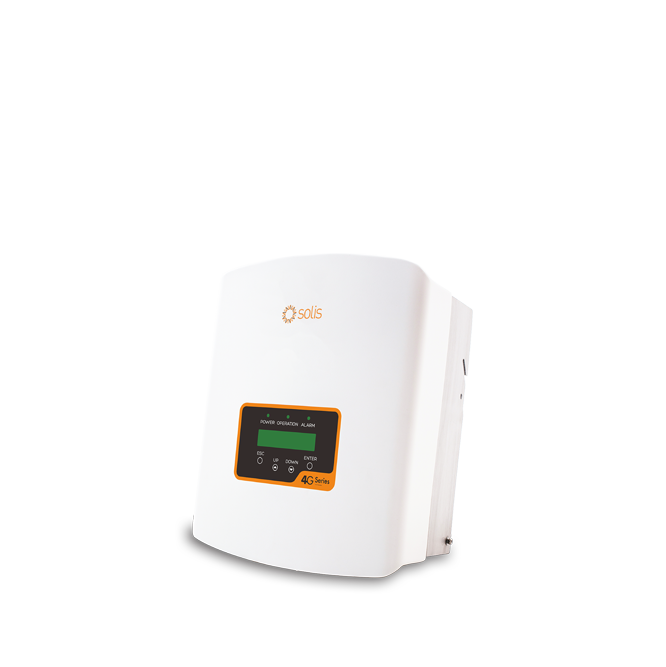 Solis-Mini(700-3600)-4G
Solis-Mini(700-3600)-4G
-
 S6-GR1P(2.5-6)K-S
S6-GR1P(2.5-6)K-S
-
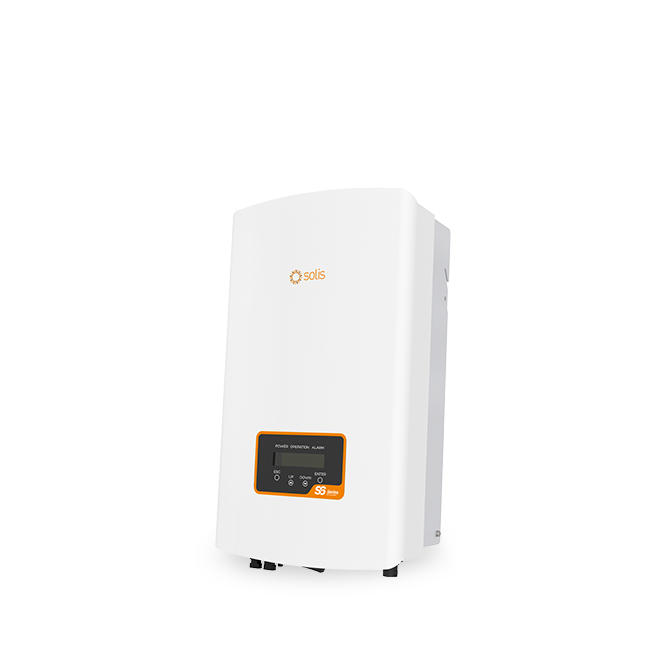 S6-GR1P(2.5-6)K
S6-GR1P(2.5-6)K
-
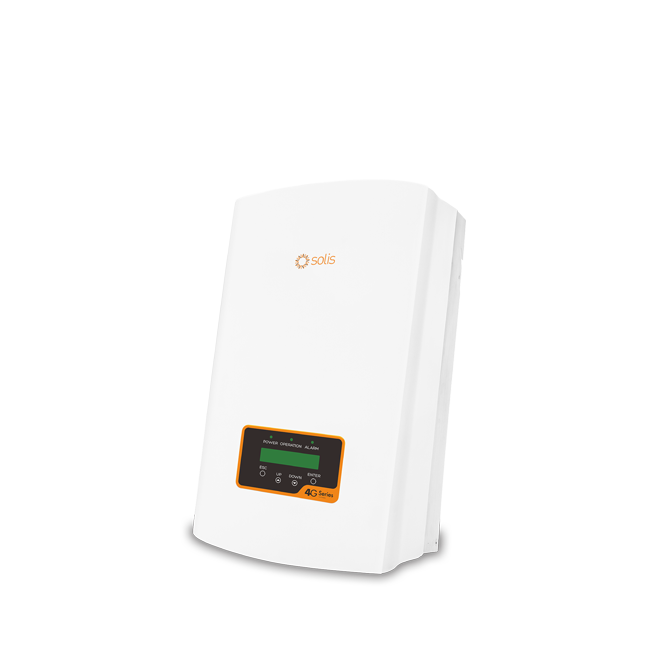 Solis-1P(2.5-6)K-4G
Solis-1P(2.5-6)K-4G
-
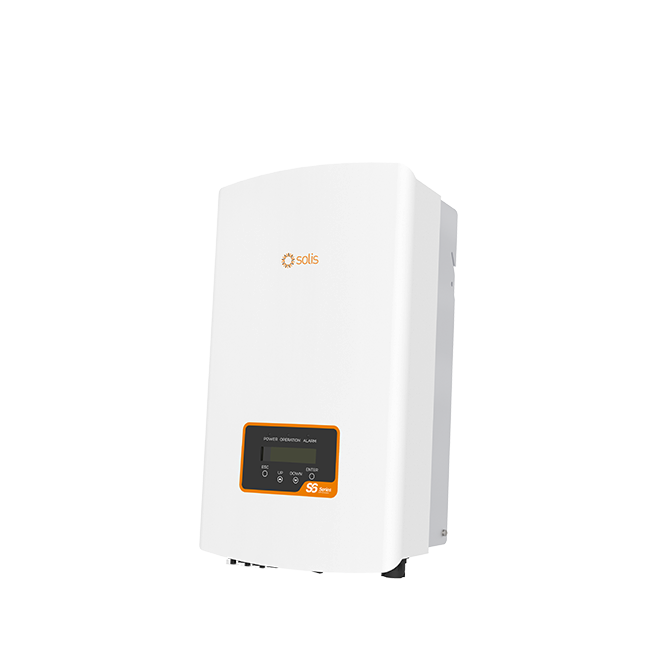 S6-GR1P(7-8)K2
S6-GR1P(7-8)K2
-
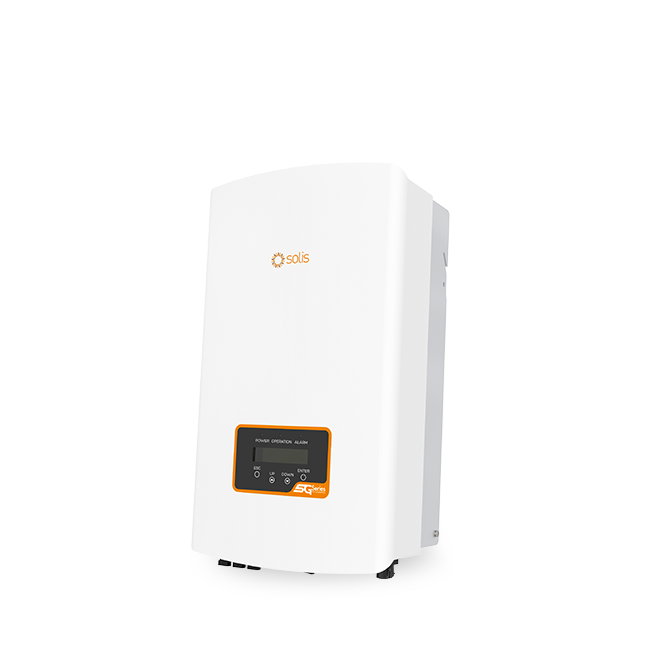 Solis-1P(7-8)K-5G
Solis-1P(7-8)K-5G
-
 S6-GR1P(8-10)K03-NV-ND
S6-GR1P(8-10)K03-NV-ND
-
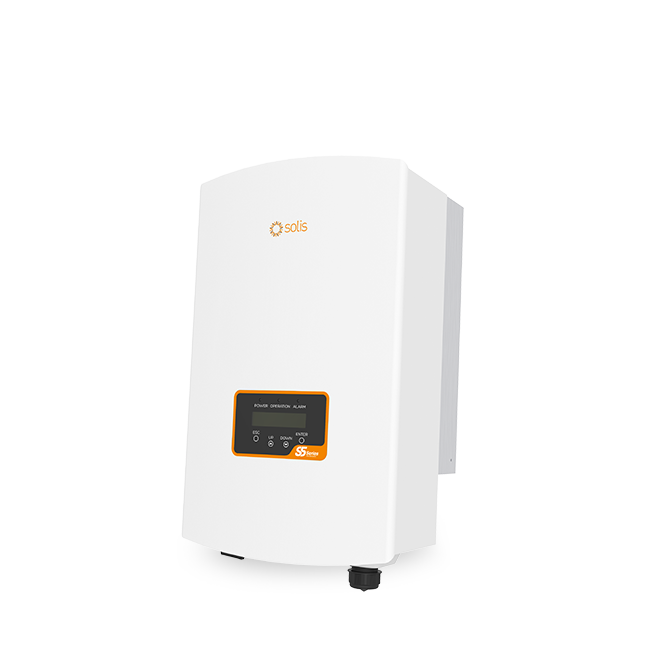 S5-GR1P(7-10)K
S5-GR1P(7-10)K
-
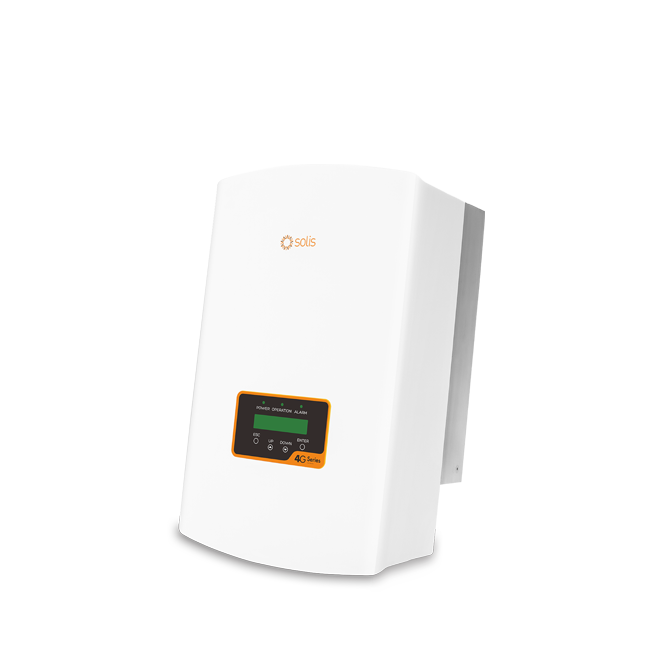 Solis-1P(9-10)K-4G
Solis-1P(9-10)K-4G
-
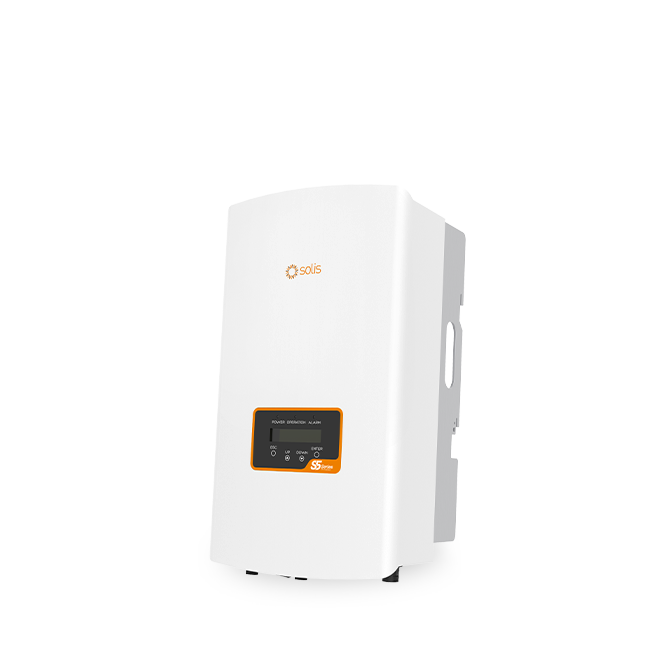 S5-GR3P(3-20)K
S5-GR3P(3-20)K
-
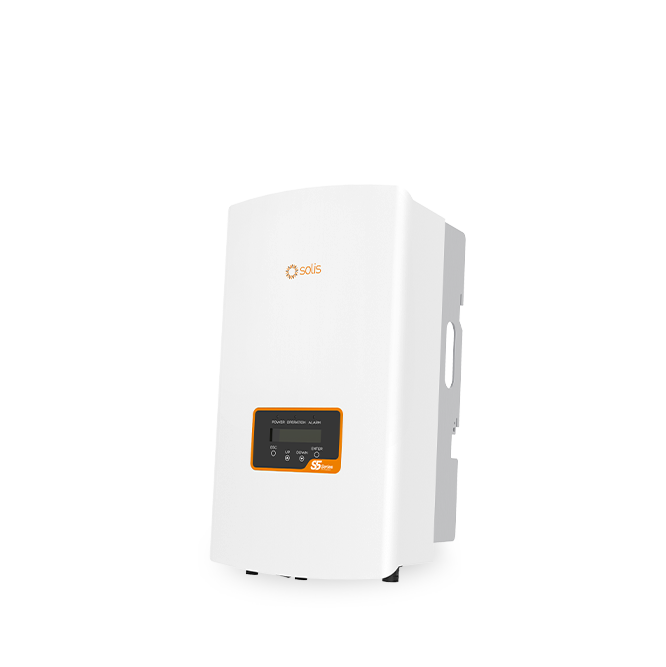 S5-GR3P(5-10)K-LV
S5-GR3P(5-10)K-LV
-
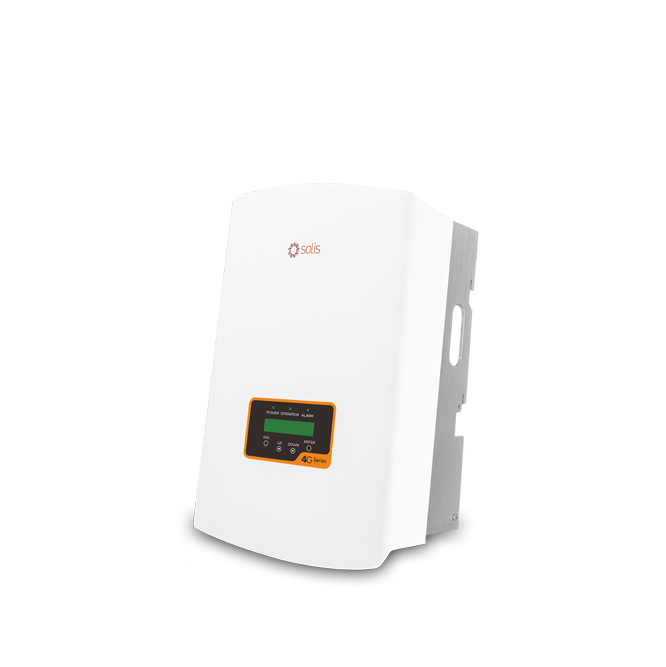 Solis-3P(3-20)K-4G
Solis-3P(3-20)K-4G
-
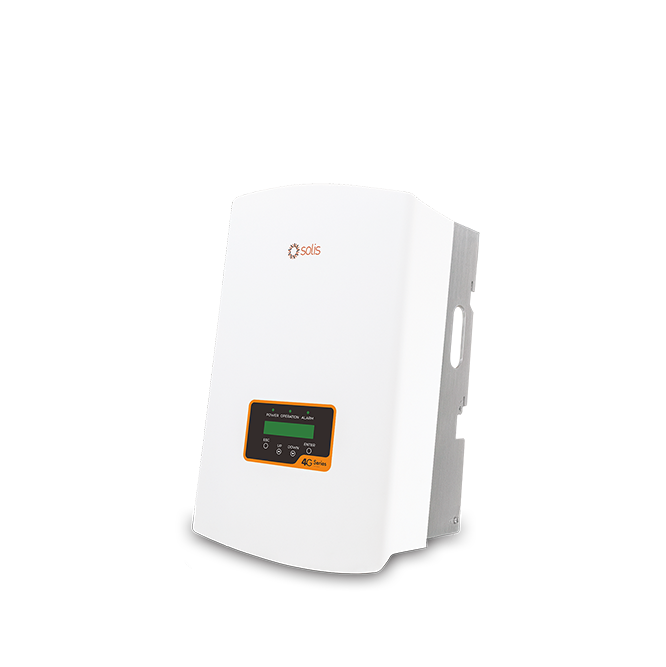 Solis-3P(5-10)K-4G-LV
Solis-3P(5-10)K-4G-LV
-
 S6-GC3P(25-40)K03-ND
S6-GC3P(25-40)K03-ND
-
 S6-GC3P(15-20)K03-LV-ND
S6-GC3P(15-20)K03-LV-ND
-
 S5-GC(25-50)K
S5-GC(25-50)K
-
 S5-GC(15-23)K-LV
S5-GC(15-23)K-LV
-
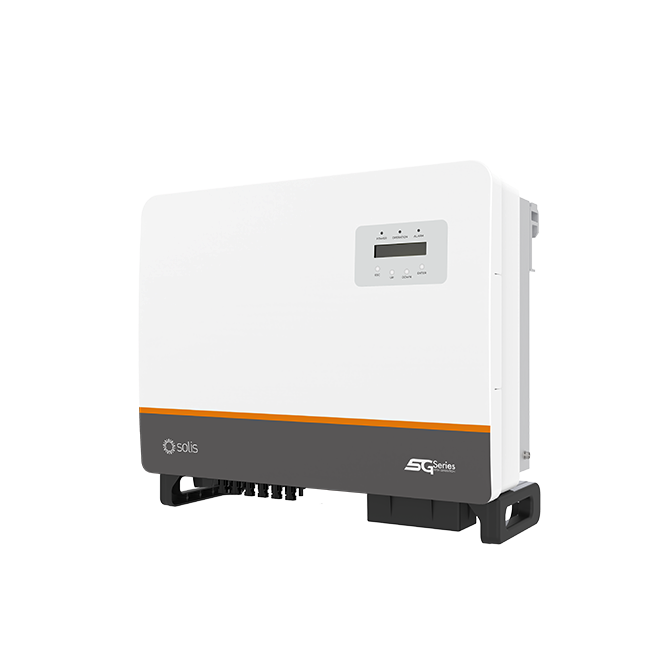 Solis-(25-50)K-5G
Solis-(25-50)K-5G
-
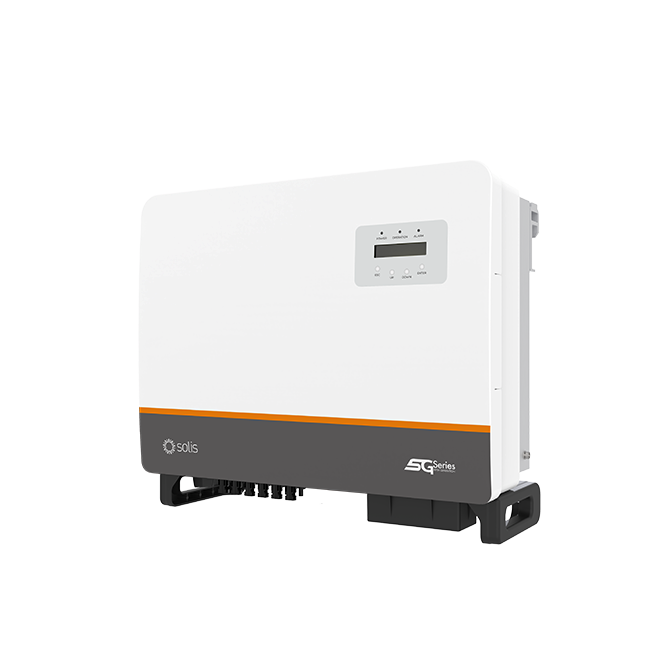 Solis-(15-23)K-LV-5G
Solis-(15-23)K-LV-5G
-
 S6-GC3P(40-60)K-ND
S6-GC3P(40-60)K-ND
-
 S6-GC3P(23-36)K-LV-ND
S6-GC3P(23-36)K-LV-ND
-
 S5-GC(50-60)K
S5-GC(50-60)K
-
 S5-GC(25-36)K-LV
S5-GC(25-36)K-LV
-
 S6-GC(80-125)K
S6-GC(80-125)K
-
 S6-GC(50-75)K-LV
S6-GC(50-75)K-LV
-
 Solis-80K-5G-PRO
Solis-80K-5G-PRO
-
 Solis-(50-75)K-LV-5G-PRO
Solis-(50-75)K-LV-5G-PRO
-
 S5-GC(80-110)K
S5-GC(80-110)K
-
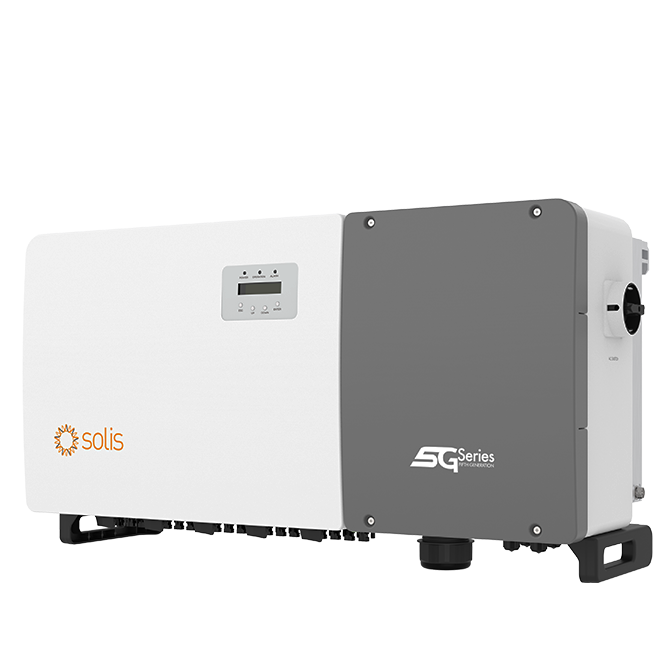 S5-GC(50-60)K-LV
S5-GC(50-60)K-LV
-
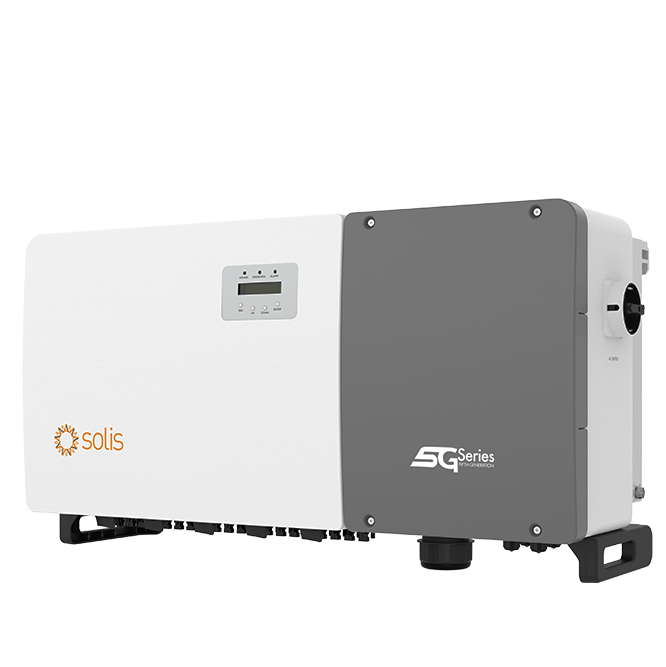 S5-GC(100-125)K
S5-GC(100-125)K
-
 S6-GC3P(150-200)K07-ND
S6-GC3P(150-200)K07-ND
-
 S6-GC3P(80-100)K07-LV-ND
S6-GC3P(80-100)K07-LV-ND
-
 Solis-(215-255)K-EHV-5G
Solis-(215-255)K-EHV-5G
-
 S6-GU350K-EHV
S6-GU350K-EHV
-
- Solution
- Service and Support
- Enterprise Explore
- About Us
- Contact Us
Select Your Region
- Asia/Pacific
-
 中国
中国
-
 India
India
-
 Việt nam
Việt nam
-
 Australia
Australia
-
 대한민국
대한민국
-
 پاکستان
پاکستان
-
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
-
Filipino
-
 Malaysia
Malaysia
-
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
-
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
-
 Indonesia
Indonesia
-
 Узбекистан
Узбекистан
- Europe
-
 Ireland
Ireland
-
 Türkiye
Türkiye
-
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
-
 France
France
-
 Deutschland
Deutschland
-
 Nederland
Nederland
-
 España
España
-
 Česká republika
Česká republika
-
 Sverige
Sverige
-
 Polska
Polska
-
 Україна
Україна
-
 Italia
Italia
-
 Português
Português
-
 България
България
-
 Magyarország
Magyarország
-
 Lietuva
Lietuva
-
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
- North America
-
 United States
United States
-
 Canada
Canada
-
 México
México
- South America
-
 Brasil
Brasil
-
 República de Chile
República de Chile
- Middle East and Africa
-
 South Africa
South Africa
-
 المملكة العربية السعودية
المملكة العربية السعودية
-
 الجمهورية اللبنانية
الجمهورية اللبنانية
-
 امارات عربية متحدة
امارات عربية متحدة
-
 اليمن
اليمن
-
 المملكة الأردنّيّة الهاشميّة
المملكة الأردنّيّة الهاشميّة
-
 جمهورية مصر العربية
جمهورية مصر العربية
-
 la République Tunisienne
la République Tunisienne
-
 Kenya
Kenya
-
 Tanzania
Tanzania
-
 Nigeria
Nigeria
- Other Countries and Regions
-
 Other Countries and Regions
Other Countries and Regions